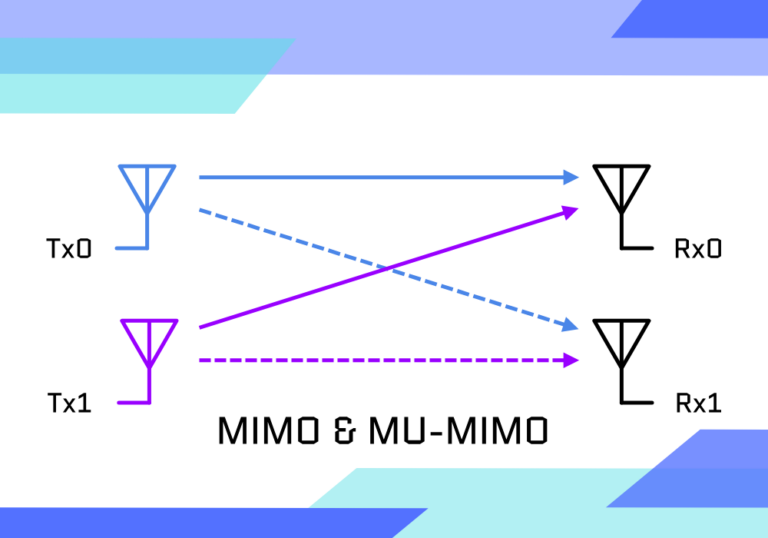
MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) and MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input, Multiple Output) are revolutionary technologies that have significantly enhanced WiFi performance. By enabling multiple data streams between devices, these innovations improve speed, capacity, and reliability. Understanding their evolution, use cases, benefits, and future prospects is key to appreciating their role in modern wireless communication.
What is Wireless MIMO?
MIMO is a wireless communication technology that uses multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to transmit and receive multiple data streams simultaneously. Introduced with the 802.11n (WiFi 4) standard, MIMO marked a breakthrough in wireless networking by increasing data throughput and improving reliability without needing additional spectrum or power.
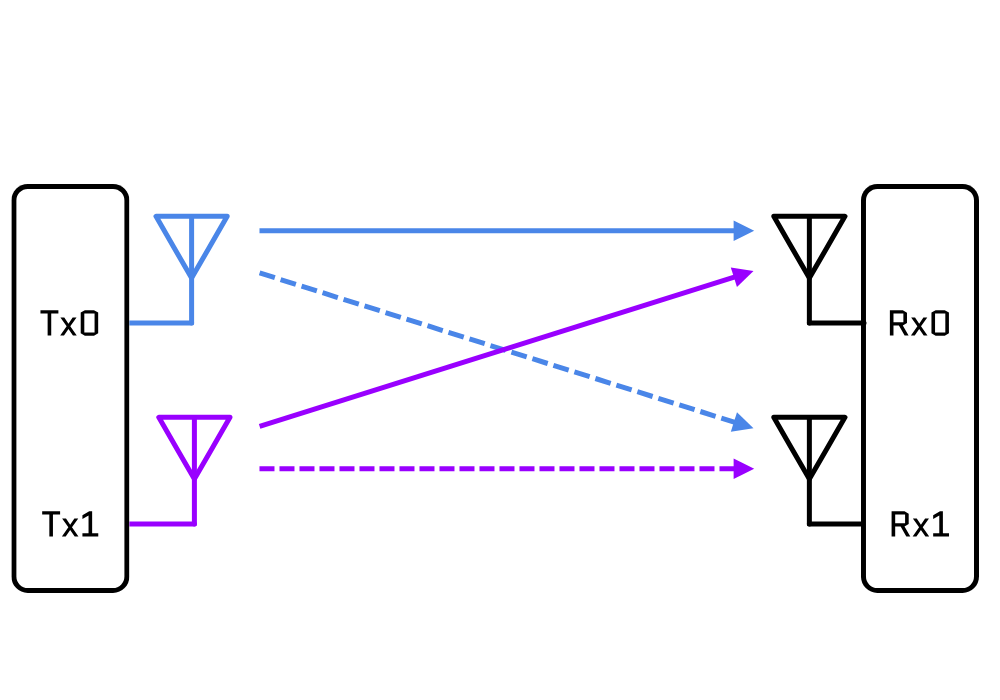
MIMO achieves this by leveraging spatial multiplexing, which splits a single data stream into multiple streams, transmitting them simultaneously over different spatial paths. This maximizes data transfer rates and ensures better performance, even in environments with signal interference or obstructions.
Use Cases for Wireless MIMO
- Home WiFi Networks: MIMO improves video streaming quality and reduces buffering.
- Enterprise Environments: Enhances capacity for high-density networks like offices or schools.
- Mobile Devices: Improves download speeds and connection reliability.
What is MU-MIMO?
MU-MIMO, an evolution of MIMO, stands for Multi-User MIMO. It was introduced with the 802.11ac (WiFi 5) standard and refined further in WiFi 6 (802.11ax). Unlike MIMO, which serves only one device at a time, MU-MIMO enables simultaneous communication with multiple devices.
For example, in traditional MIMO, a router sends data sequentially to devices, leading to potential bottlenecks in multi-device environments. MU-MIMO eliminates this limitation by allowing the router to serve multiple devices at once, significantly increasing network efficiency.
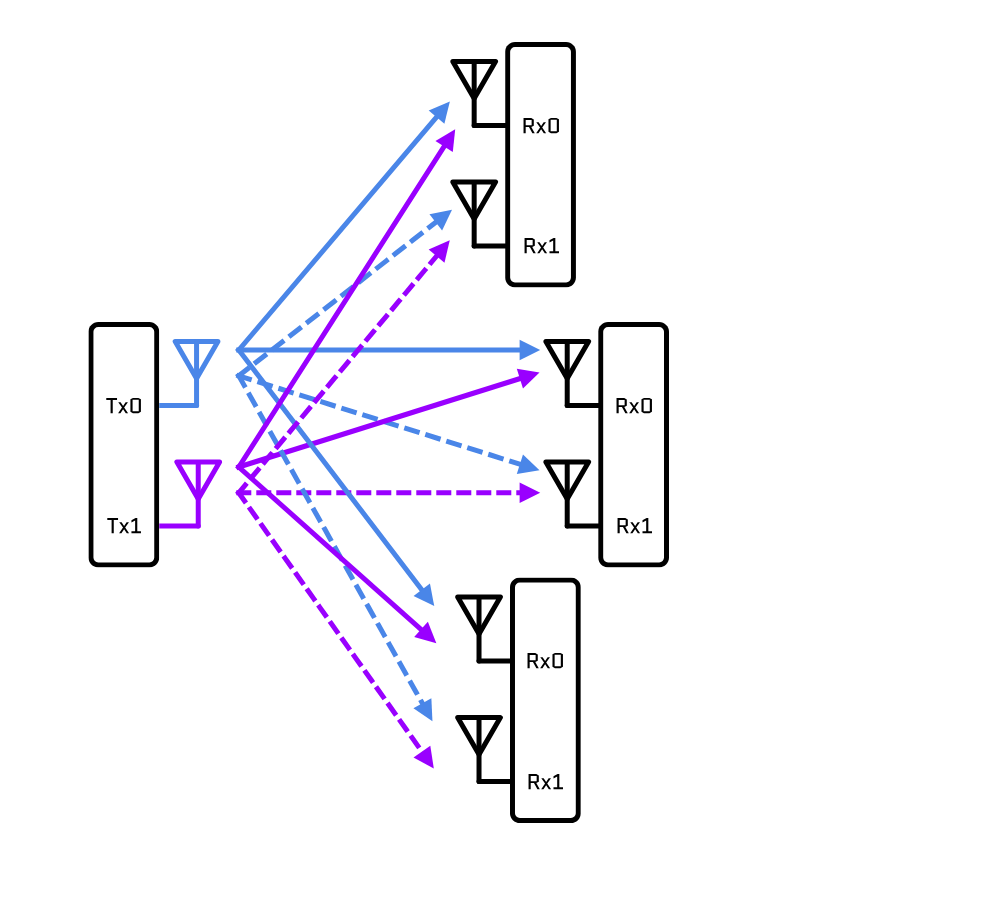
Use Cases for MU-MIMO
- Smart Homes: Ideal for homes with numerous IoT devices like smart TVs, cameras, and thermostats.
- Streaming and Gaming: Enhances performance for multiple users streaming HD content or gaming simultaneously.
- Enterprise Networks: Supports high-demand environments like conferences or stadiums.
Evolution of MIMO and MU-MIMO
- WiFi 4 (802.11n): Introduced MIMO with up to 4×4 configurations (4 transmit and 4 receive antennas), enabling faster speeds and improved range.
- WiFi 5 (802.11ac): Introduced MU-MIMO for downlink communication, supporting up to 4 simultaneous users.
- WiFi 6 (802.11ax): Extended MU-MIMO to both uplink and downlink, supporting up to 8 streams and significantly improving multi-device performance.
Benefits of MIMO and MU-MIMO
- Improved Speeds: MIMO increases data rates, while MU-MIMO optimizes bandwidth for multiple devices.
- Better Range and Reliability: Multiple antennas ensure stronger signals and reduced dead zones.
- Enhanced Network Efficiency: MU-MIMO minimizes latency and bottlenecks in multi-user environments.
- Scalability: Essential for growing IoT ecosystems and enterprise networks.
Future of MIMO and MU-MIMO
The future of MIMO and MU-MIMO lies in advancing WiFi 7 (802.11be), which aims to push wireless speeds beyond 30 Gbps. Expected innovations include:
- Higher Antenna Configurations: Supporting even more streams for ultra-high-speed applications.
- Enhanced Spectrum Usage: Combining MU-MIMO with 160 MHz and 320 MHz channel widths for unprecedented throughput.
- Integration with 6GHz Band: Expanding capacity for dense, high-performance environments.
Additionally, MIMO and MU-MIMO will play a crucial role in 5G networks, ensuring robust connectivity for mobile and IoT devices in increasingly complex environments.
Conclusion
MIMO and MU-MIMO have transformed wireless networking by enabling faster speeds, better reliability, and greater efficiency. While MIMO laid the groundwork for enhanced communication, MU-MIMO has taken it a step further, addressing the challenges of multi-device connectivity. As WiFi standards continue to evolve, these technologies will remain foundational, shaping the future of wireless communication in smart homes, enterprises, and beyond.