What is IPv6?
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It was developed to replace IPv4, which has been around since the early days of the internet.
🌍 Why do we need IPv6?
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, which gives about 4.3 billion unique IP addresses. That seemed like a lot in the 1980s, but with modern devices (phones, tablets, laptops, smart TVs, smart fridges, IoT devices…) — we ran out of IPv4 addresses.
IPv6 solves this problem by using 128-bit addresses, which gives us:
👉 340 undecillion addresses (that’s 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456!)
🧠 How does IPv6 look?
IPv6 addresses are written as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons :.
Example:
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334You can shorten it (remove leading zeros and collapse consecutive zeros) like:
2001:db8:85a3::8a2e:370:7334⚙️ IPv6 Features
- ✅ Huge Address Space
No more running out of IP addresses. - ✅ Simpler Routing
More efficient and scalable, especially for ISPs. - ✅ Built-in Security
IPSec (encryption and authentication) is mandatory. - ✅ No More NAT
Devices can have globally unique addresses, so no need for Network Address Translation. - ✅ Better Multicast and Anycast Support
Efficient delivery of data to multiple destinations.
🏡 IPv6 Address Types
- Unicast — one-to-one communication (like IPv4).
- Multicast — one-to-many (IPv6 replaces IPv4’s broadcast).
- Anycast — one-to-nearest (used for things like DNS servers).
🔥 Quick Comparison: IPv4 vs IPv6
| Feature | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Address size | 32-bit | 128-bit |
| Address example | 192.168.1.1 | 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334 |
| Address count | ~4.3 billion | ~340 undecillion |
| NAT | Often required | Typically not needed |
| Security | Optional (IPSec) | Built-in |
| Configuration | Manual / DHCP | Auto-configuration (SLAAC) |
💡 How IPv6 Assigns Addresses
- Link-local (starts with
fe80::) — for communication inside the same network link. - Global Unicast (starts with
2xxx:or3xxx:) — public addresses. - Unique Local (starts with
fc00::/7) — like private IPv4 (10.0.0.0/8or192.168.0.0/16).
ISP Prefix (DHCPv6 Client)
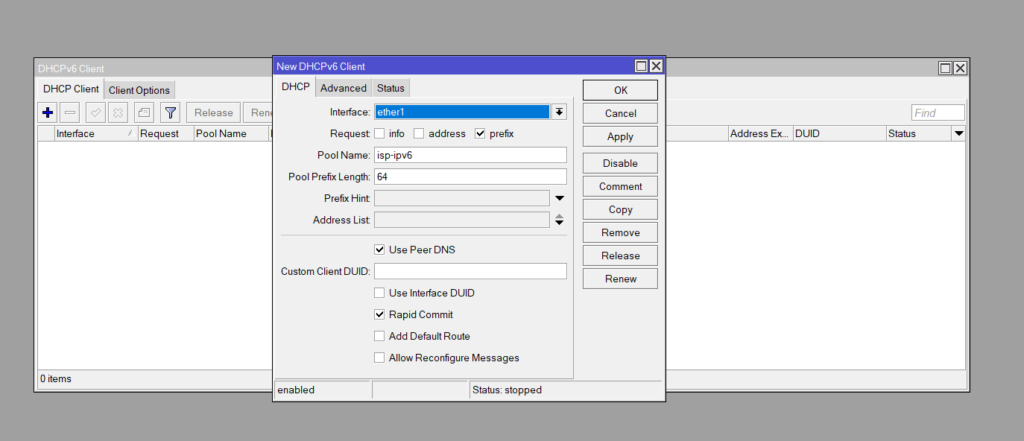
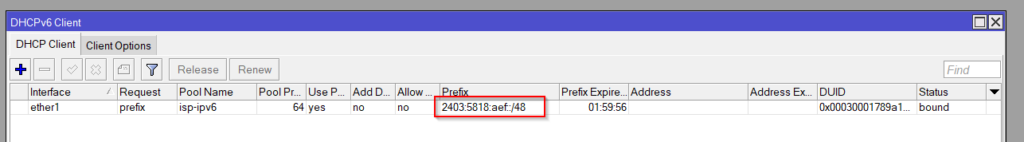
Our ISP Provided Prefix is: 2403:5818:aef::/48
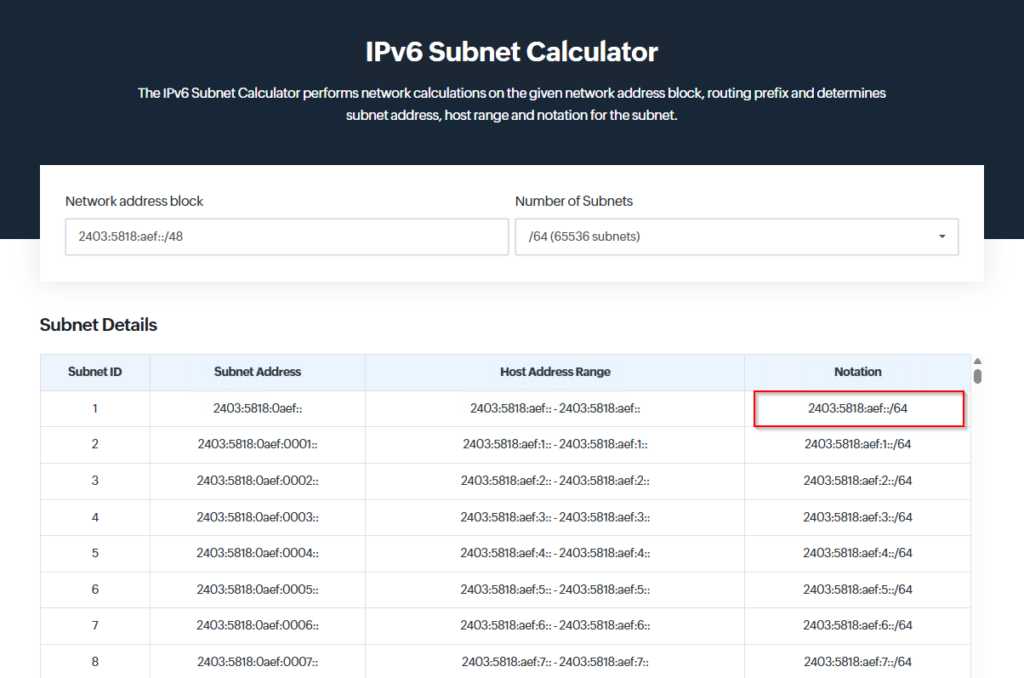
Create LAN subnet from prefix
Simplest way is to use an online IPv6 Subnet Calculator. Use the first /64 from the prefix:
https://www.site24x7.com/tools/ipv6-subnetcalculator.html
Assign IP to LAN
From the subnet use the first host as the IP for the LAN :1
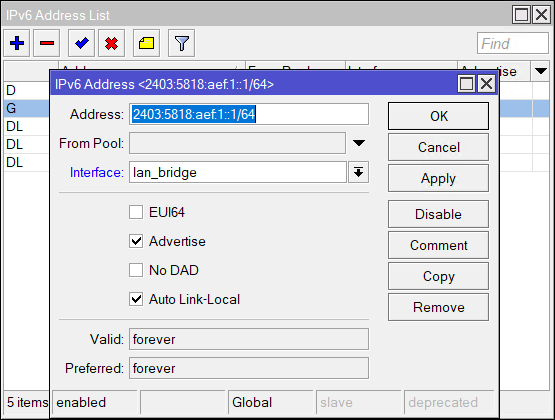
Client IP Assignment (Neighbour Discovery)
Instead of DHCP for IP assignment in IPv4, use the Neighbour Discovery to advertise the range to the clients. Select the interface as the LAN bridge (lan_bridge). Unlick Advertise MAC Address and tick Other Configuration.